Antibody-drug conjugate targeting tumour-associated macrophages as a cancer treatment

M2-type macrophages secreting large amounts of anti-inflammatory factors (such as IL-10) to form an immunosuppressive microenvironment, thereby helping the tumour cells escape immune surveillance, and accelerating their recurrence and metastasis
Hindered T-cell migration towards and within the tumour site due to tumour immunosuppressive microenvironment, resulting in the low availability of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes and progressive tumour growth.
In clinical settings, TAMs as prognostic markers for multiple cancer recurrences after surgery, including non-small cell lung cancer, gastric cancer, and non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours.
Competitive advantages
- 6-25 mAb very specific to M2 (does not recognise type 1 macrophages, other cells of the immune system, or healthy cells)
- Very good affinity of 6-25 mAb for its target R6-25 hence:
- very few side effects, and no resistance to treatments
- restoration of the effectiveness of the immune system, and inhibition of the angiogenesis
- M2 cancer existing treatments either non-specific or causing significant side effects
- No clinical trial drug candidate specifically targeting R6-25
Applications
Targeted therapy against AML strongly expressing R6-25 or immunotherapy targeting M2 such as:
- non-small cell lung cancer
- pancreatic cancer
- bladder cancer
- prostate cancer
- ovarian cancer
Intellectual property
Patent
Development stage
Experimental proof of concept
Description
Monoclonal antibody (6-25) specfically targeting macrophage type-2 through the receptor R6-25
=> Production of antibodies against Nurse Like Cells (NLC), the TAMs in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL)
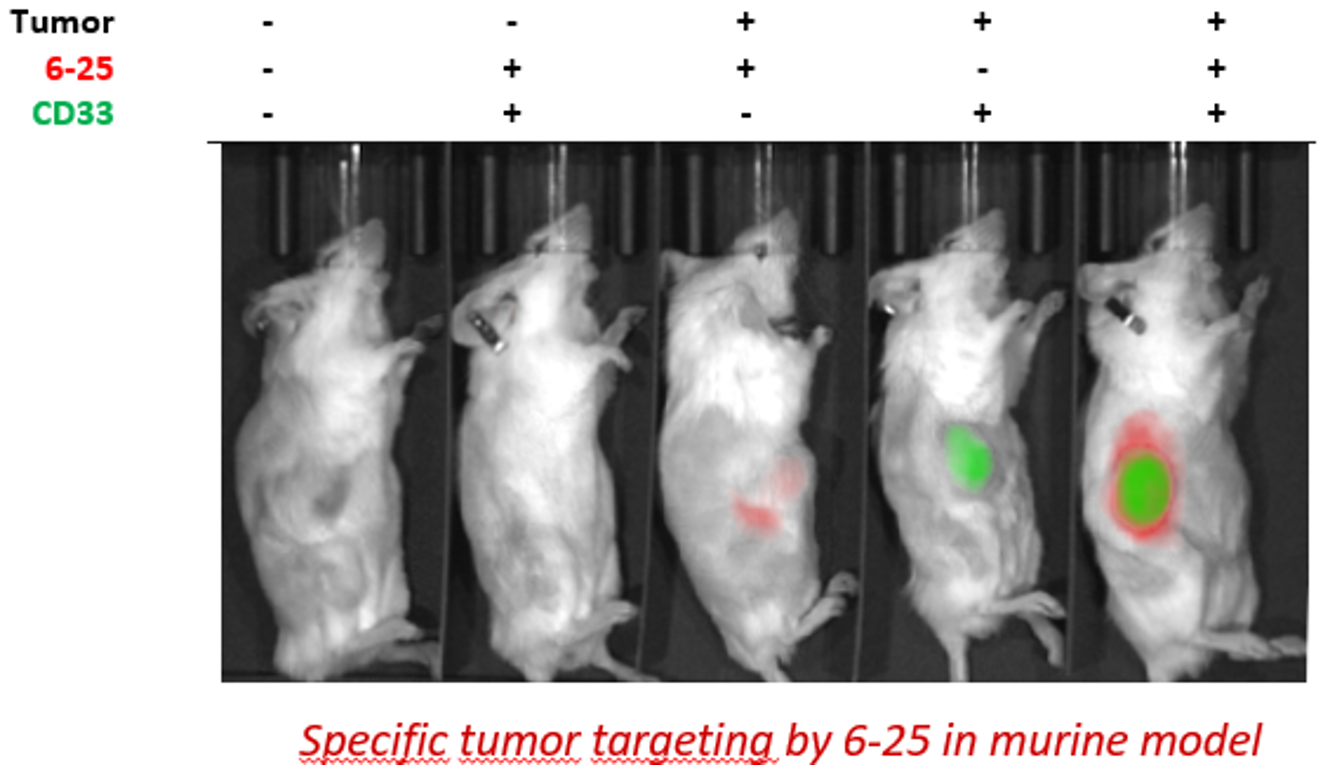
Technical specifications
Membrane receptor identification (named R6-25 ):
- For immune cells only retrieved in Type-2 macrophages
- Biacore analysis: KD6-25 = 12.75 pM
Experiment performed on NLC (tumoral macrophages):
- Verification of antibody specificity (type-1 versus type-2 macrophages), internalisation for ADC production, and targeting in vivo on tumour cells
- Toxicity against type-2 macrophages - no toxicity against type-1 macrophages and other cells



