There are a number of possible treatments for cancer. These treatments can be used in combination, depending on the type of cancer and the stage of the disease. The most widely developed medications are currently immunotherapies, which target certain receptors on the surface of T lymphocytes to induce an immune response. They are much more specific and have fewer side effects, but they are very expensive and many patients do not respond to immunotherapy or relapse. This failure is partly due to the fact that there are many different receptors that can 'bypass' the action of these antibodies.
Competitive advantages
- Means of reactivating the immune system to fight against tumours
- Specificity of drug candidates
- Target of choice for acting on several ICIs at the same time, limiting tumour cell escape mechanisms and side effects
Applications
- Treatment of solid cancers
Intellectual property
- Patent
Development stage
Validation of the technology in a real environment
Laboratory
CRCT INSERM
Description
New small chemical molecules capable of inhibiting the expression of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) while preserving the effector functions and proliferation of T lymphocytes
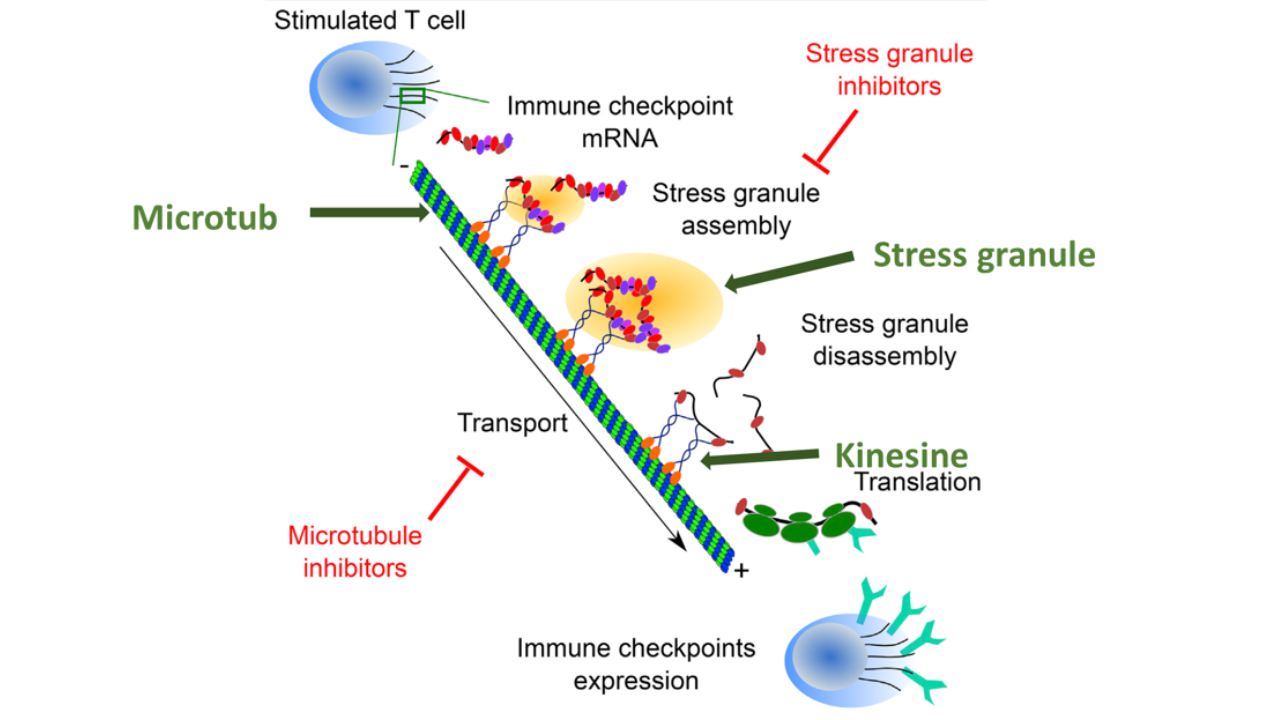
Demonstration of the mechanisms regulating ICI expression at the plasma membrane: T lymphocytes control the expression of these membrane receptors by associating the mRNAs encoding these ICIs with stress granules. Inhibiting the formation of these stress granules simultaneously blocks the expression of several ICIs on the surface of T lymphocytes. Using a cell-based assay, several families of compounds capable of blocking the expression of these ICIs without affecting the viability and functions of these T lymphocytes were identified.
Technical specifications
- In vitro inhibition of ICI in human lymphocytes (PD-1, TIM3, LAG3)
- Post-transcriptional inhibition (no impact on ICI mRNA)
- Inhibition of stress granule life cycles
- No inhibition of lymphocyte activity (survival, immune functions not affected)
- POC in animal models underway




